Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
A diagram illustrating different types of price elasticity of demand: perfectly inelastic, perfectly elastic, and unitary elastic demand curves.
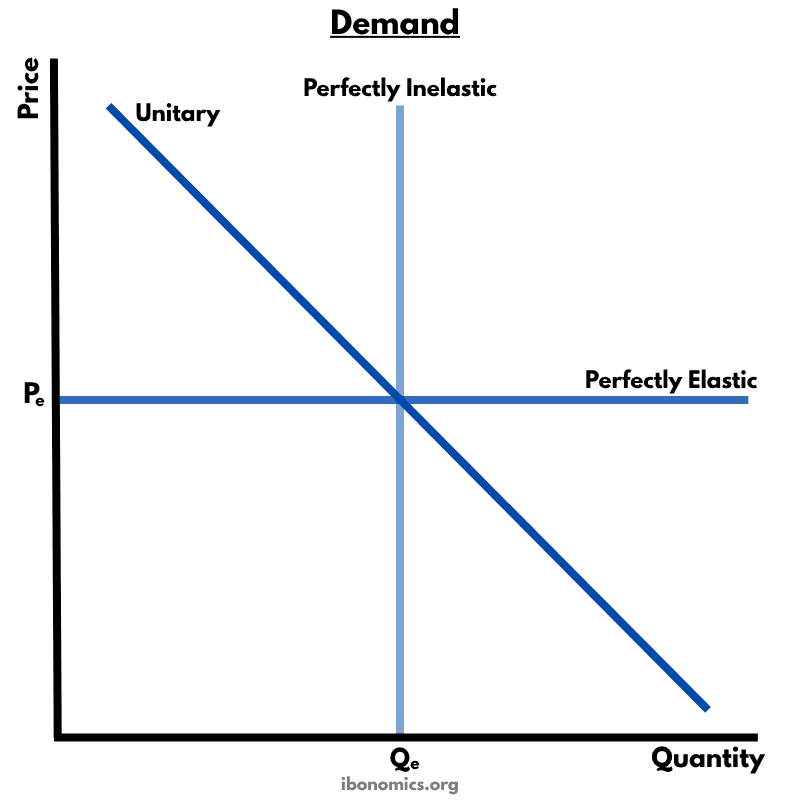
Perfectly Inelastic Demand: Vertical line — quantity demanded is completely unresponsive to price (PED = 0).
Perfectly Elastic Demand: Horizontal line — consumers will only buy at one price (PED = ∞).
Unitary Elastic Demand: Downward-sloping curve where total revenue is constant at all points (PED = 1).
The diagram shows three key types of price elasticity of demand, which measure how quantity demanded responds to changes in price.
A perfectly inelastic demand curve is vertical, indicating that quantity demanded does not change at all when price changes (PED = 0).
A perfectly elastic demand curve is horizontal, indicating that consumers are only willing to purchase at one price, and quantity demanded drops to zero if the price changes (PED = ∞).
A unitary elastic demand curve has a constant elasticity of 1, meaning the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price.
Understanding elasticity helps firms set prices and helps policymakers predict consumer responses to taxes and subsidies.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding
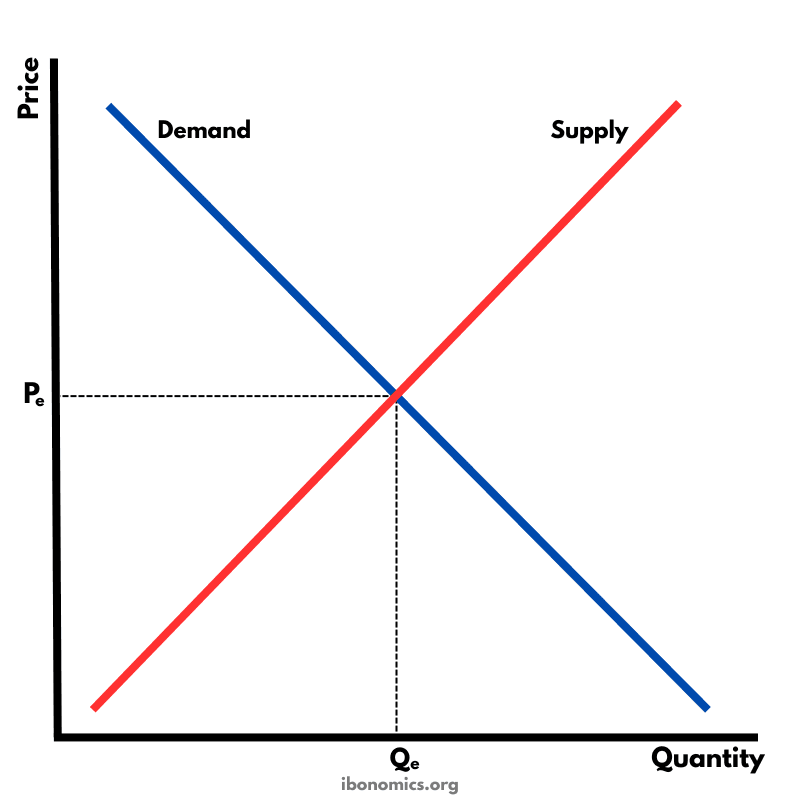
The fundamental diagram showing the relationship between demand and supply in a competitive market, determining equilibrium price and quantity.
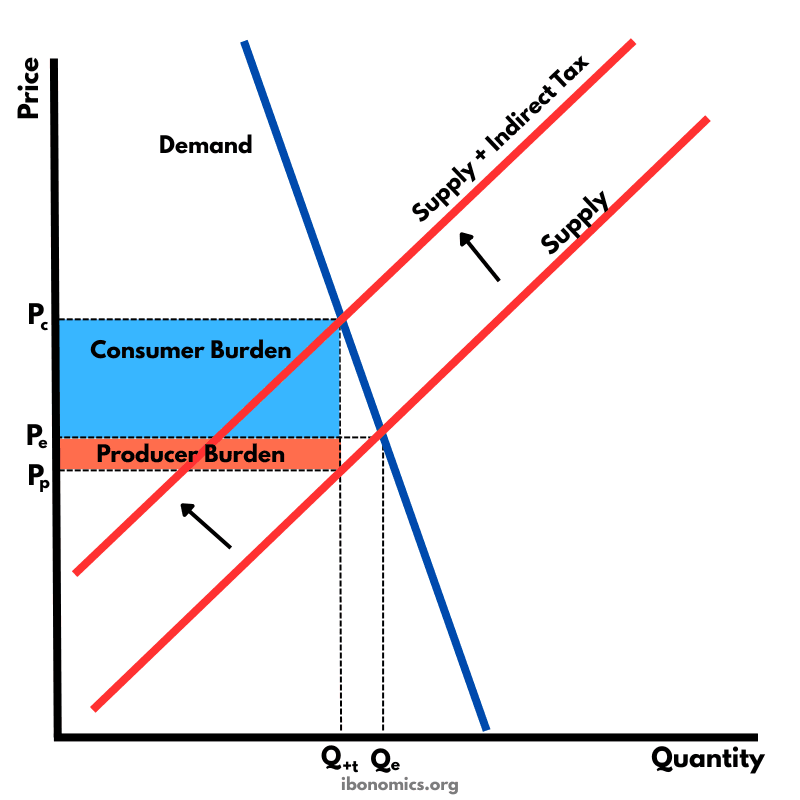
A supply and demand diagram showing the effect of an indirect tax on a good with inelastic demand. The consumer bears a larger share of the tax burden.
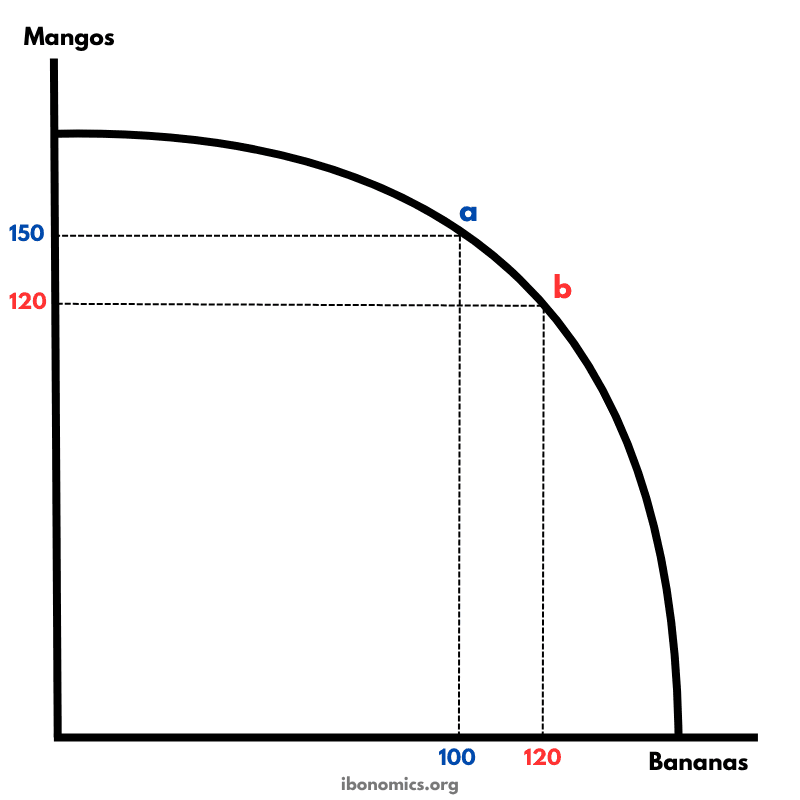
A production possibility curve illustrating the concept of opportunity cost and the trade-offs between producing two goods: mangos and bananas.
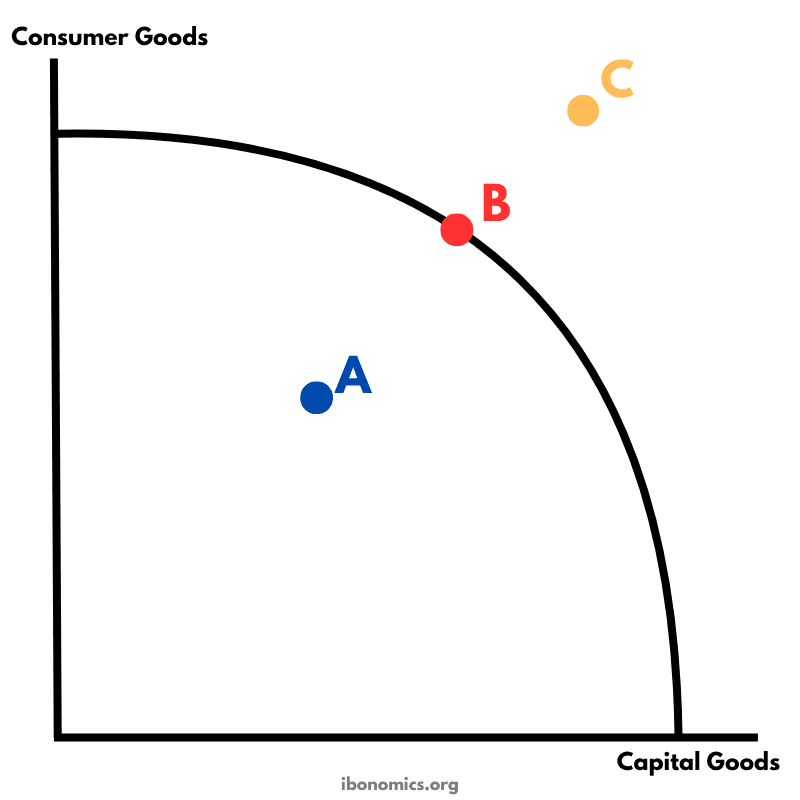
A PPC diagram showing different levels of production efficiency and economic feasibility using combinations of consumer and capital goods.
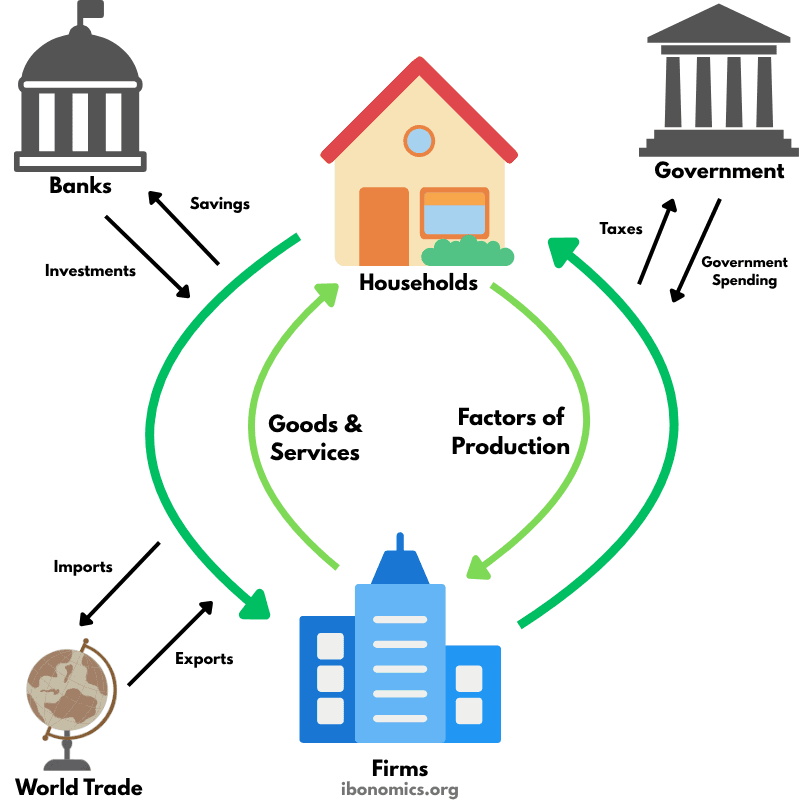
A model illustrating how money, goods, services, and resources flow between households, firms, the government, the financial sector, and the foreign sector in an economy.
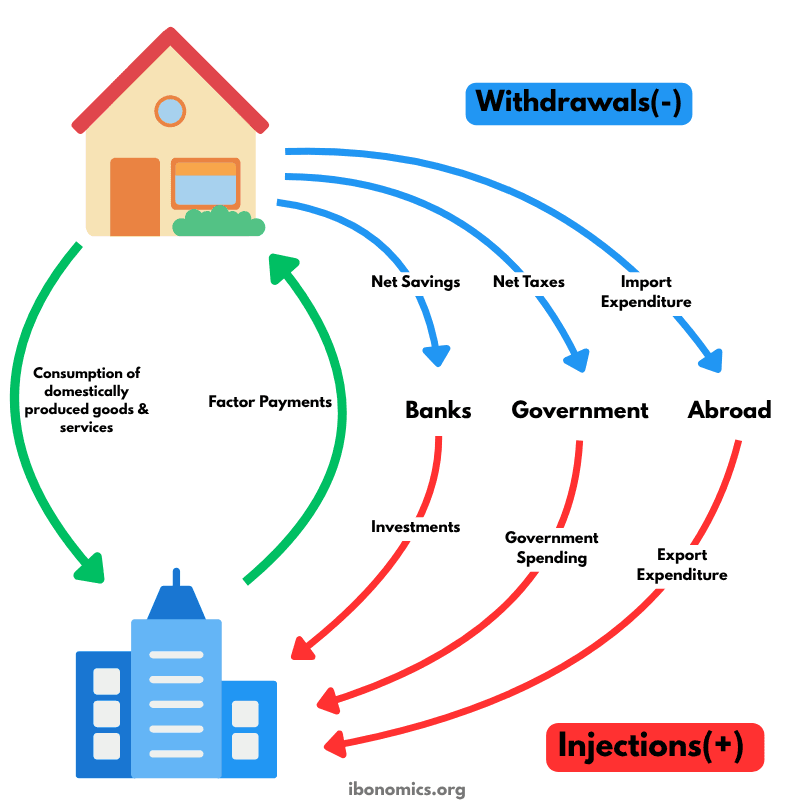
A refined circular flow model highlighting the roles of injections and withdrawals in determining national income and economic equilibrium.