Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
A diagram illustrating a positive externality of production, where the marginal social cost (MSC) is lower than the marginal private cost (MPC), leading to underproduction and welfare loss.
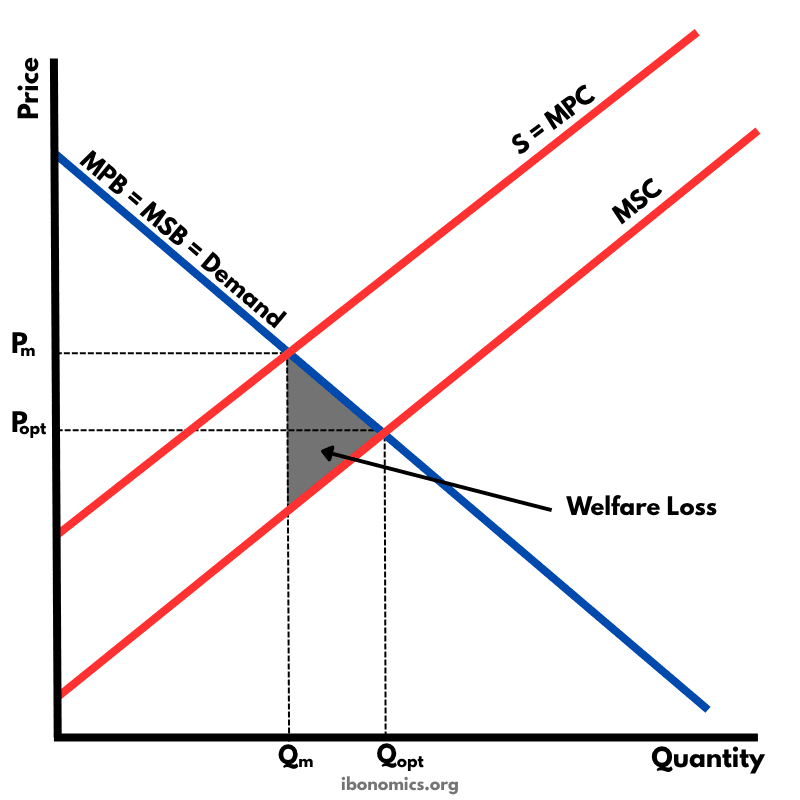
Demand Curve (MPB = MSB): Represents marginal private and social benefit, assuming no externalities in consumption.
MPC (S): Marginal private cost — the cost borne by producers.
MSC: Marginal social cost — the lower true cost to society, including external benefits.
Price Effect: The socially optimal price (Popt) is lower than the market price (Pm).
Quantity Effect: The free market underproduces (Qm) compared to the socially optimal quantity (Qopt).
Welfare Loss: The triangle representing the deadweight loss due to underproduction caused by unaccounted external benefits.
Positive externalities of production occur when a firm's output generates external benefits to third parties that are not reflected in market prices.
In the free market equilibrium, firms produce at Qm where marginal private cost (MPC) equals marginal private benefit (MPB), resulting in price Pm.
However, the socially optimal output is Qopt, where marginal social cost (MSC) equals marginal social benefit (MSB).
Because MSC < MPC, the market underproduces (Qm < Qopt), and too few resources are allocated to the good.
The shaded triangle represents welfare loss — the benefit to society that is lost due to the lower level of production.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding
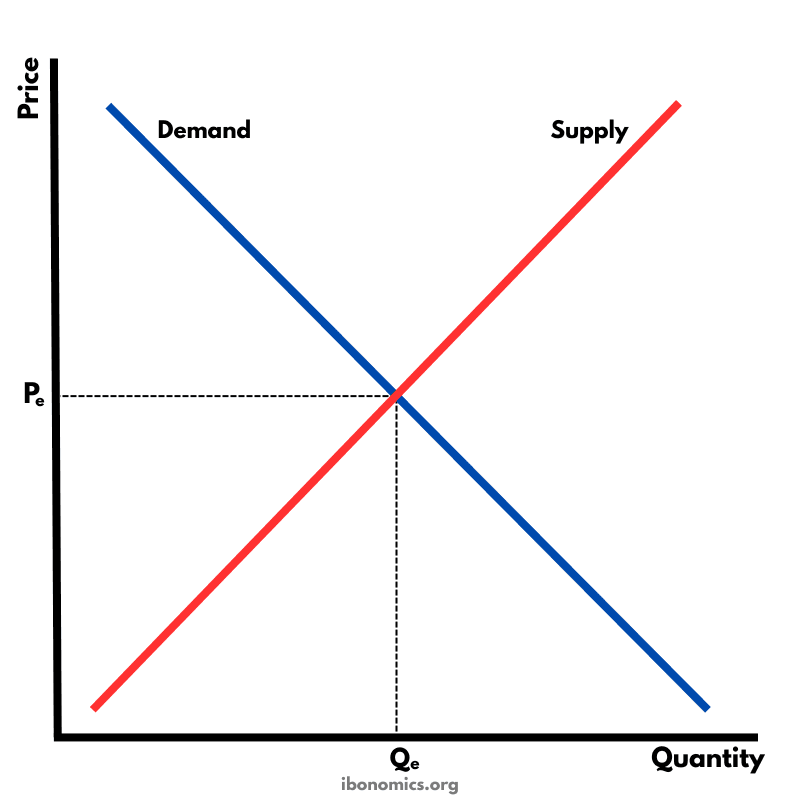
The fundamental diagram showing the relationship between demand and supply in a competitive market, determining equilibrium price and quantity.
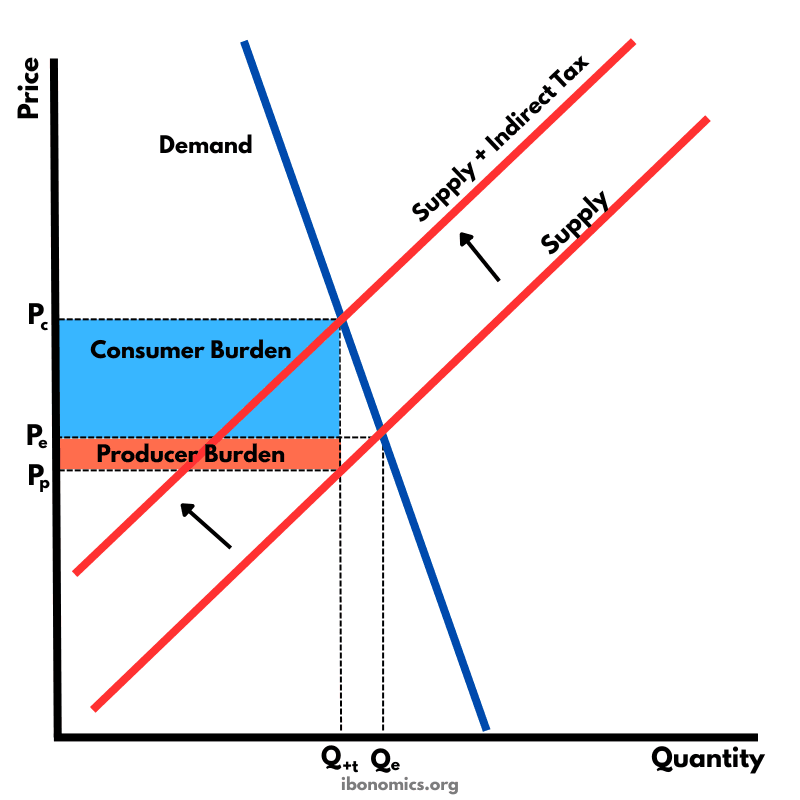
A supply and demand diagram showing the effect of an indirect tax on a good with inelastic demand. The consumer bears a larger share of the tax burden.
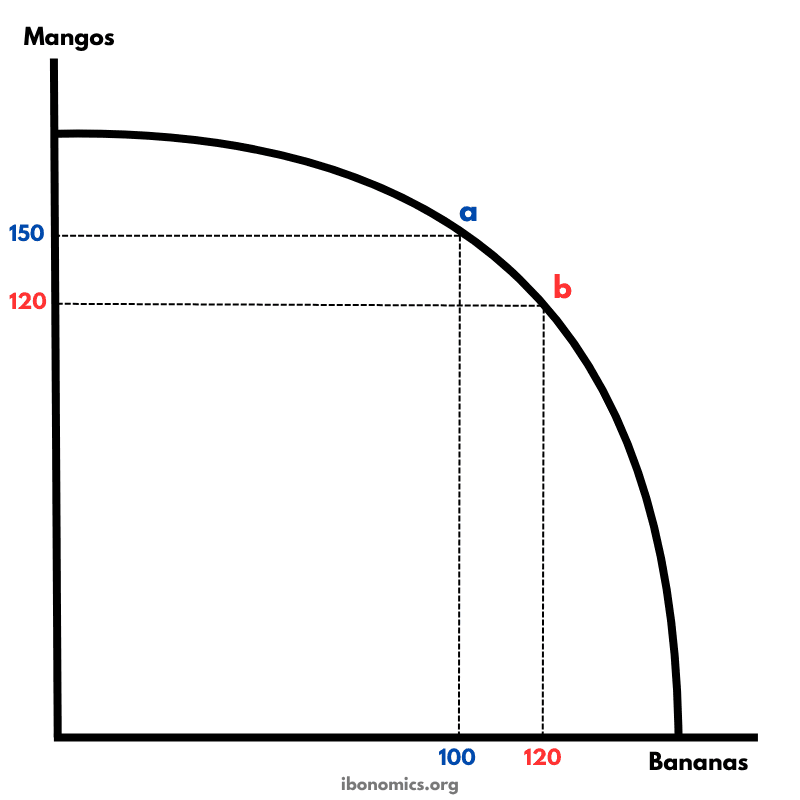
A production possibility curve illustrating the concept of opportunity cost and the trade-offs between producing two goods: mangos and bananas.
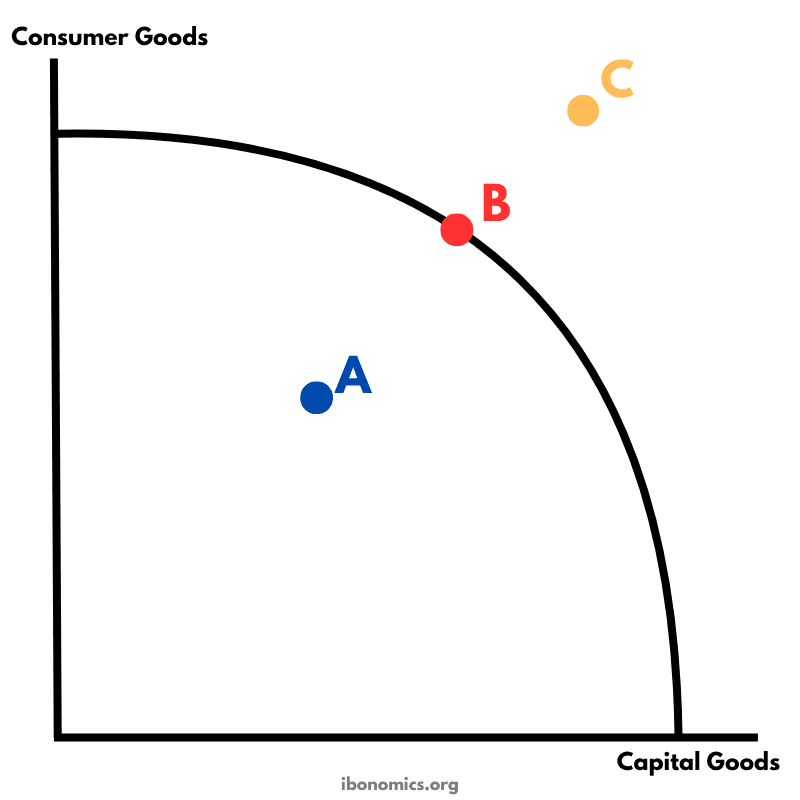
A PPC diagram showing different levels of production efficiency and economic feasibility using combinations of consumer and capital goods.
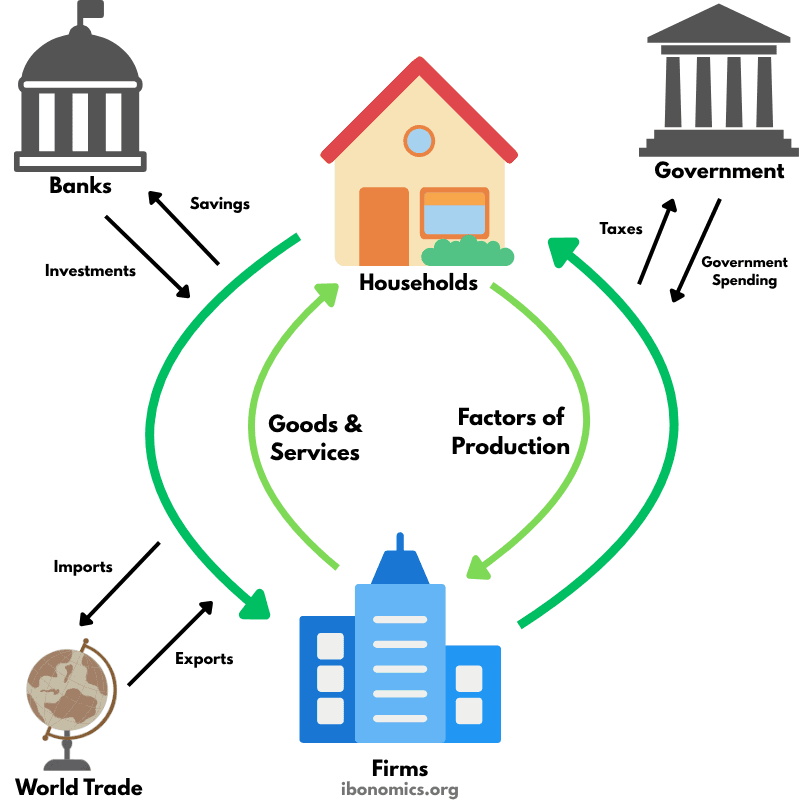
A model illustrating how money, goods, services, and resources flow between households, firms, the government, the financial sector, and the foreign sector in an economy.
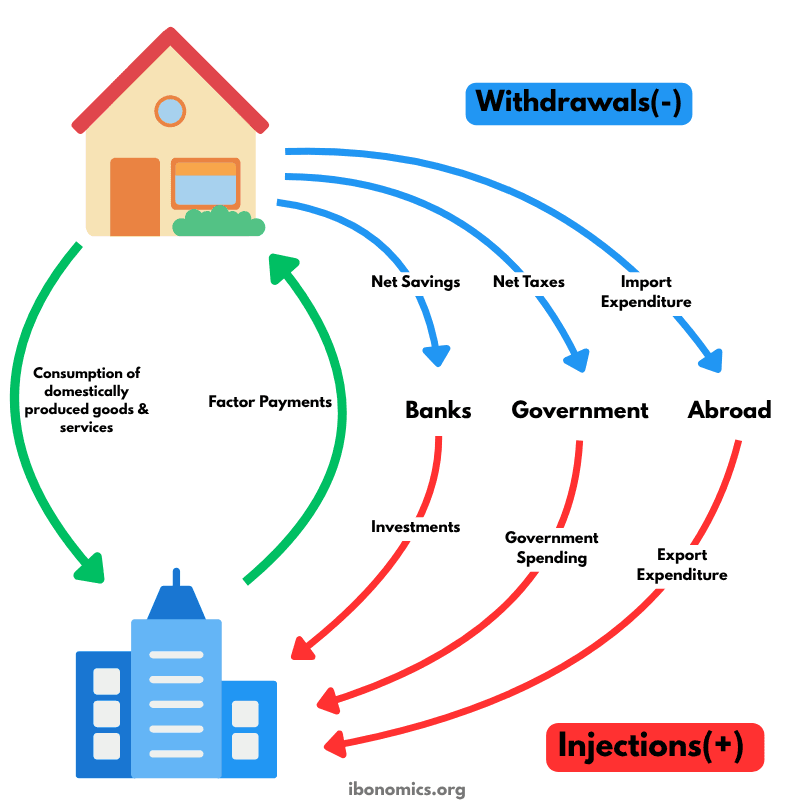
A refined circular flow model highlighting the roles of injections and withdrawals in determining national income and economic equilibrium.