Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
A diagram illustrating a firm in monopolistic competition in long-run equilibrium, where it earns normal profit. The ATC curve is tangent to the demand curve (AR), meaning total revenue equals total cost.
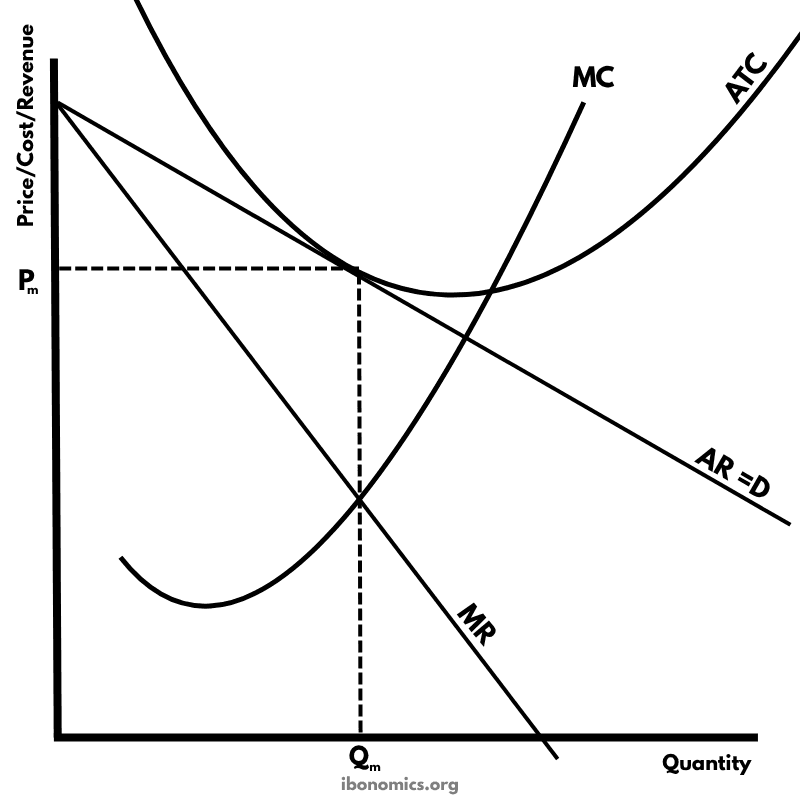
AR = D: The average revenue or demand curve, downward sloping due to product differentiation.
MR: Marginal Revenue, lies below AR because the firm must lower price to sell more.
MC: Marginal Cost, intersects MR at the profit-maximizing output Qm.
ATC: Average Total Cost, tangent to AR at Qm, indicating zero economic profit.
Qm: The output level where MR = MC.
Pm: The price corresponding to Qm on the AR curve.
Firms in monopolistic competition face a downward-sloping demand curve (AR = D) due to product differentiation.
The profit-maximizing quantity is found where marginal cost (MC) equals marginal revenue (MR).
The corresponding price (Pm) is determined by extending a line from Qm up to the AR curve.
In the long run, the ATC curve is tangent to the AR curve at Qm, indicating that the firm earns normal profit (no economic profit).
This outcome results from the entry of new firms eroding any abnormal profits that existed in the short run.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding
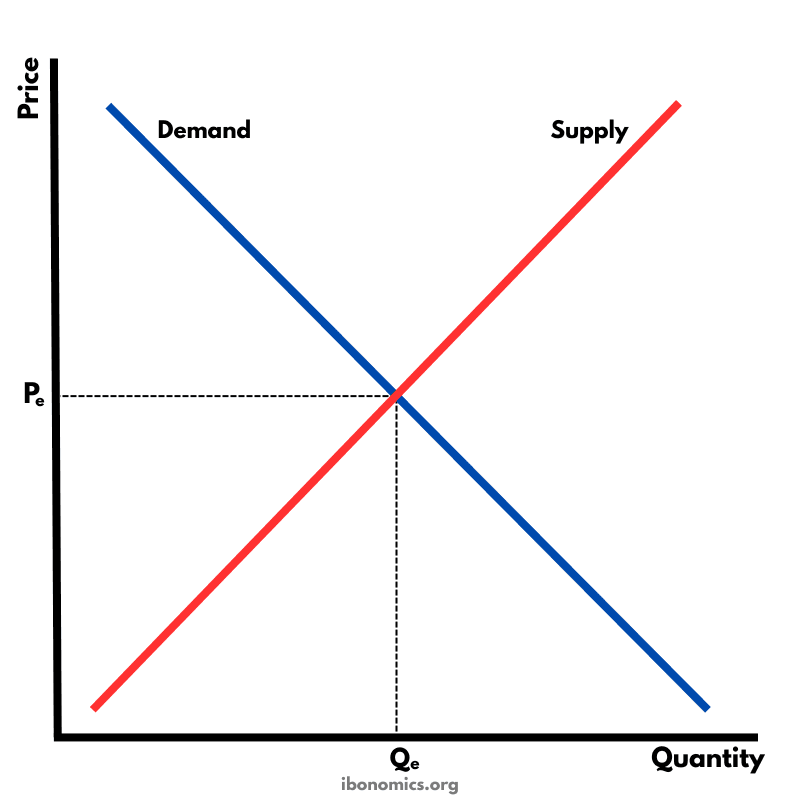
The fundamental diagram showing the relationship between demand and supply in a competitive market, determining equilibrium price and quantity.
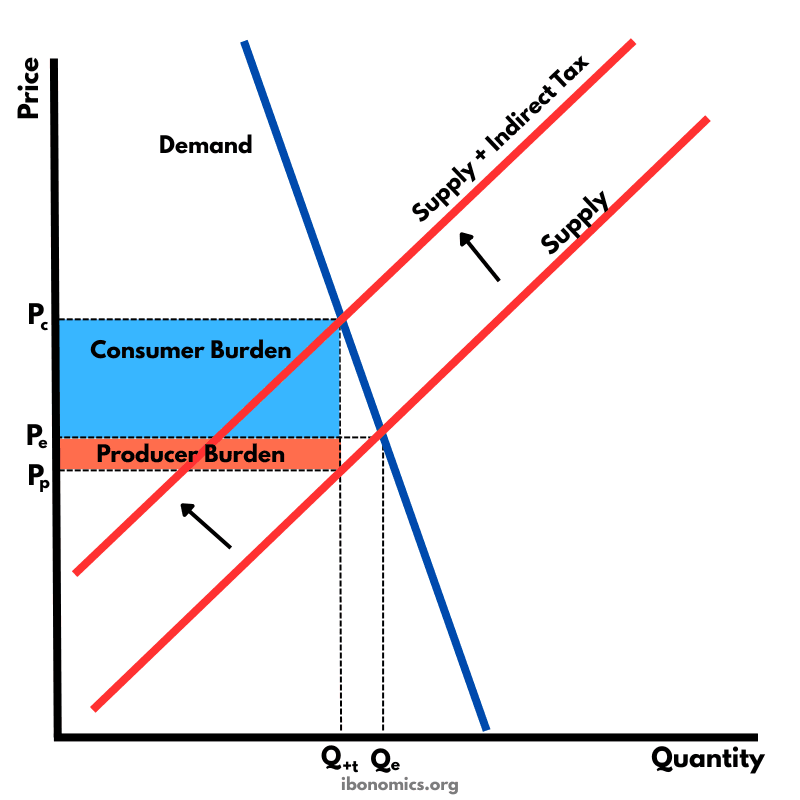
A supply and demand diagram showing the effect of an indirect tax on a good with inelastic demand. The consumer bears a larger share of the tax burden.
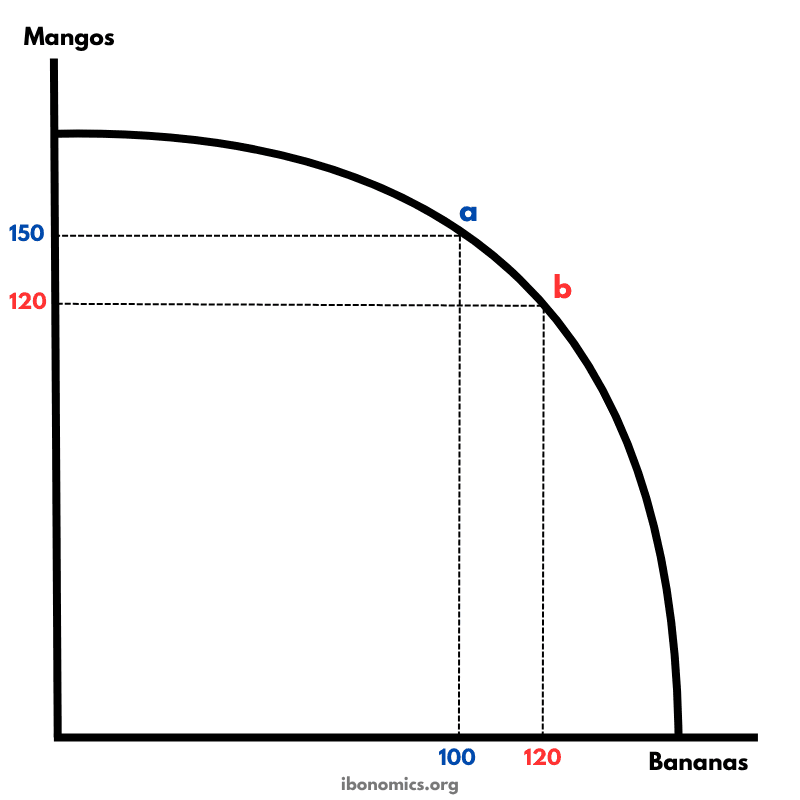
A production possibility curve illustrating the concept of opportunity cost and the trade-offs between producing two goods: mangos and bananas.
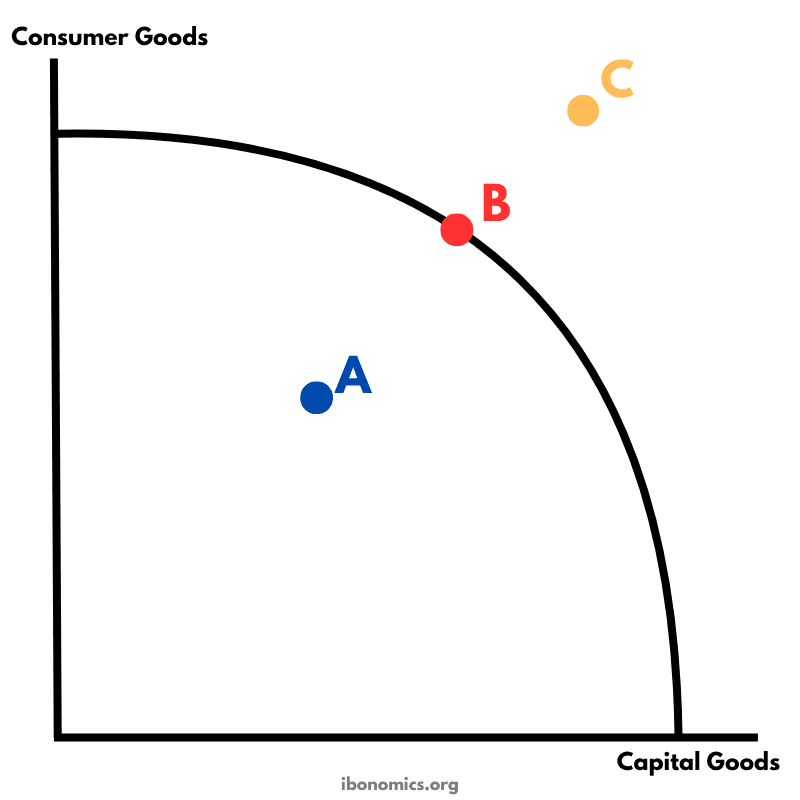
A PPC diagram showing different levels of production efficiency and economic feasibility using combinations of consumer and capital goods.
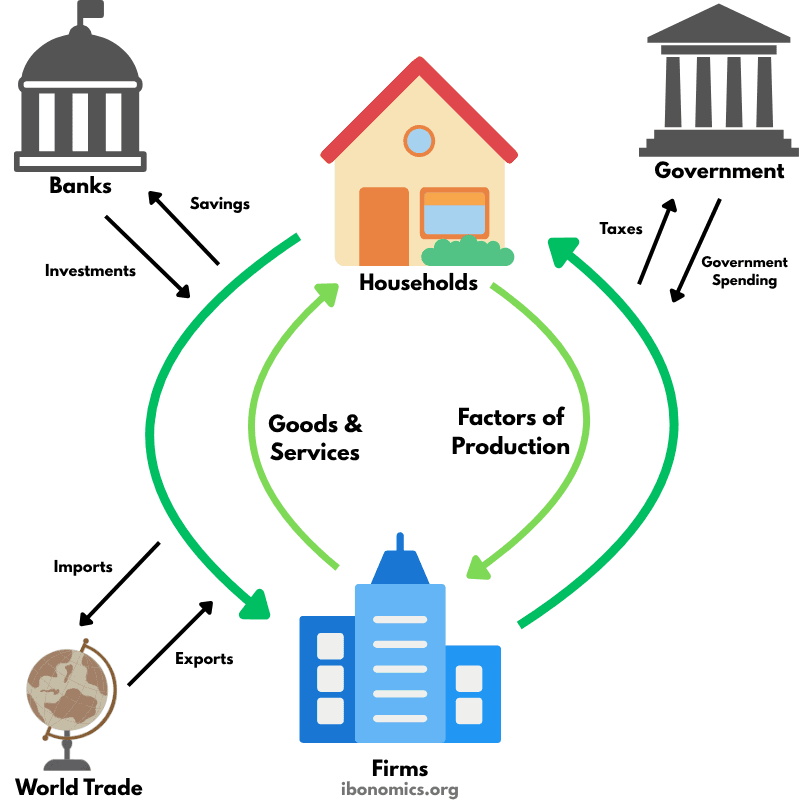
A model illustrating how money, goods, services, and resources flow between households, firms, the government, the financial sector, and the foreign sector in an economy.
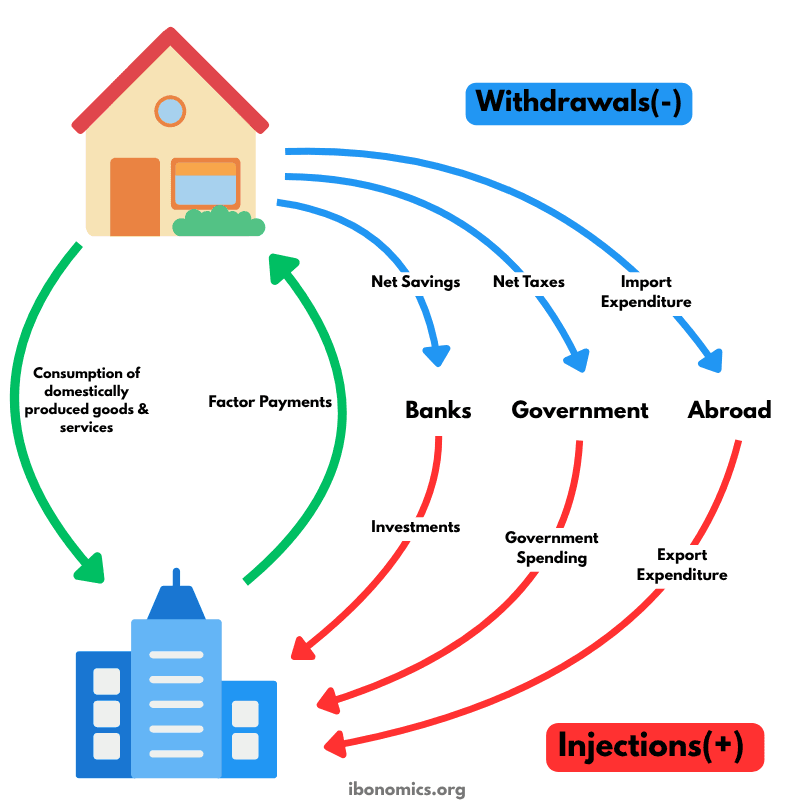
A refined circular flow model highlighting the roles of injections and withdrawals in determining national income and economic equilibrium.