Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
The Engel Curve illustrates how the quantity demanded of a good changes as consumer income changes, distinguishing between normal and inferior goods.
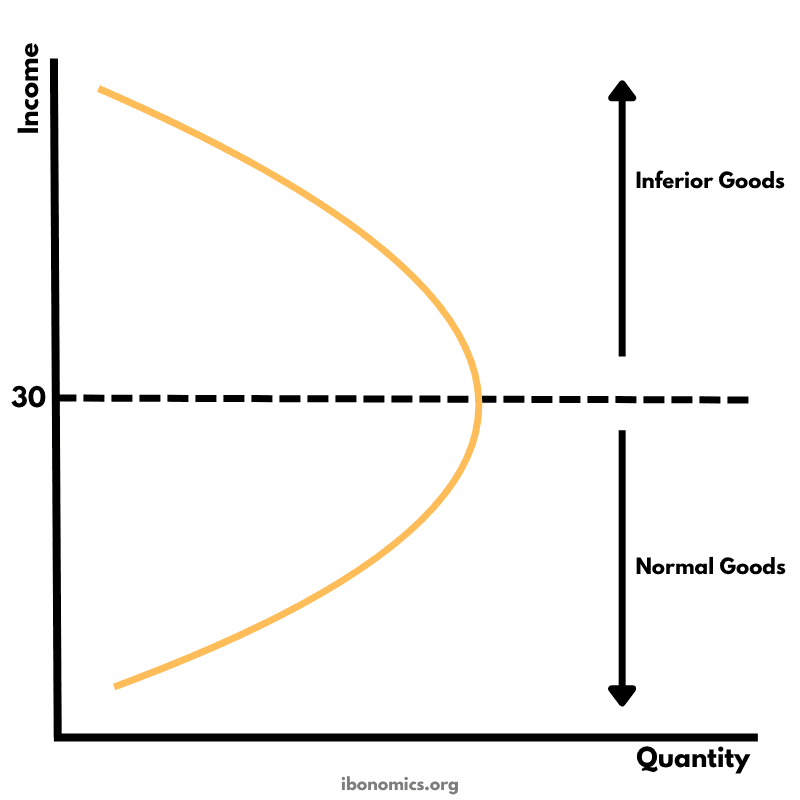
Engel Curve: Illustrates how the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to changes in consumer income.
Normal Goods: Demand increases with rising income. Represented by the upward-sloping section of the curve.
Inferior Goods: Demand decreases with rising income. Represented by the downward-sloping section of the curve.
The curve shows the relationship between a consumer's income and the quantity of a good they purchase.
For normal goods, as income increases, quantity demanded also increases — shown by the upward-sloping section of the curve below income level 30.
For inferior goods, quantity demanded decreases as income increases — seen in the downward-sloping section above income level 30.
Goods may switch from being normal to inferior at a certain income threshold, depending on consumer preferences.
Understanding Engel curves helps policymakers and businesses predict changes in demand as income levels shift across the economy.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding
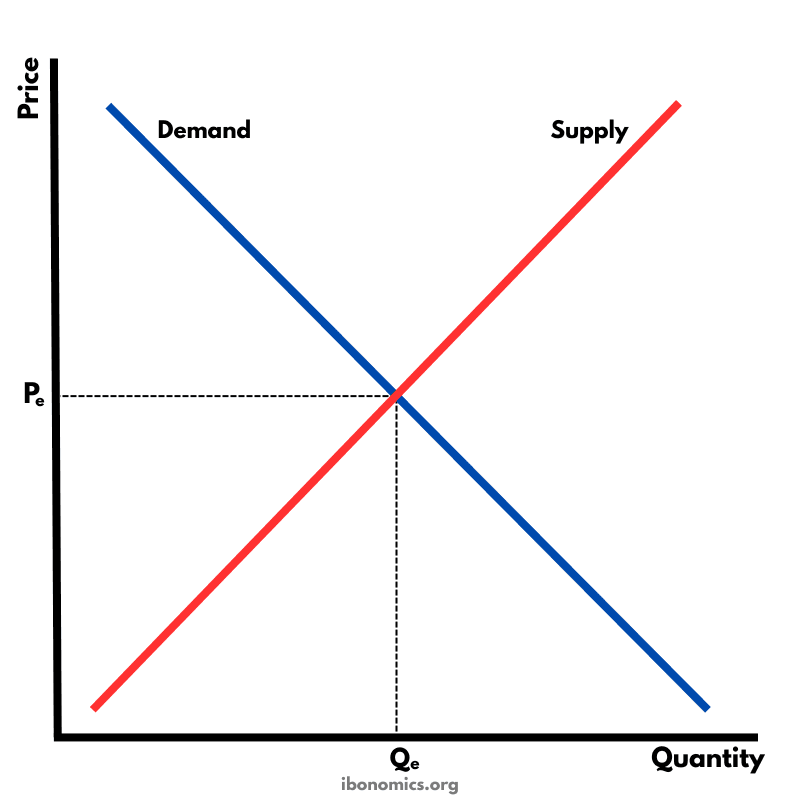
The fundamental diagram showing the relationship between demand and supply in a competitive market, determining equilibrium price and quantity.
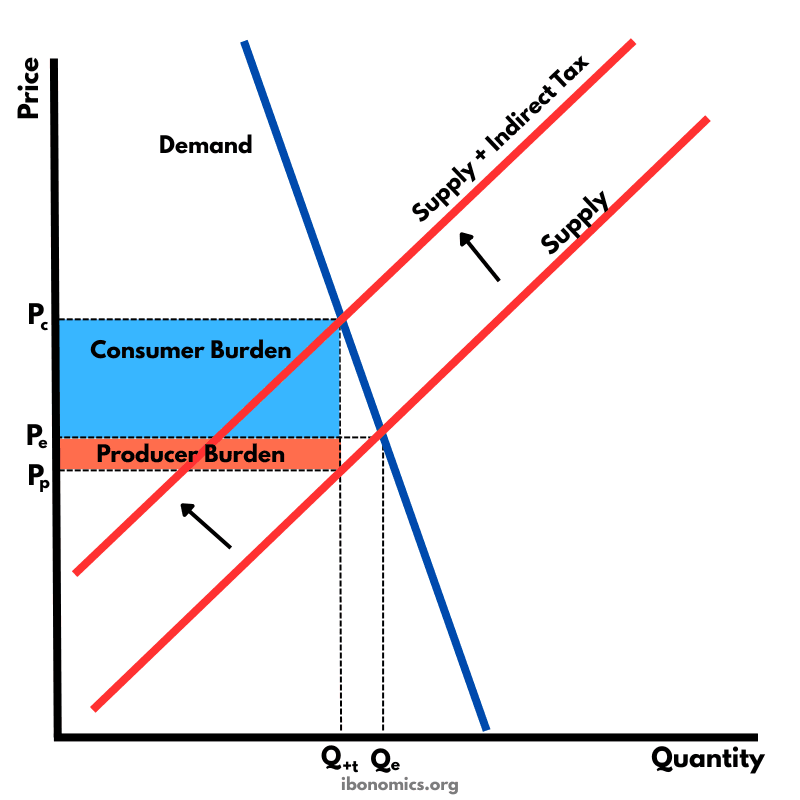
A supply and demand diagram showing the effect of an indirect tax on a good with inelastic demand. The consumer bears a larger share of the tax burden.
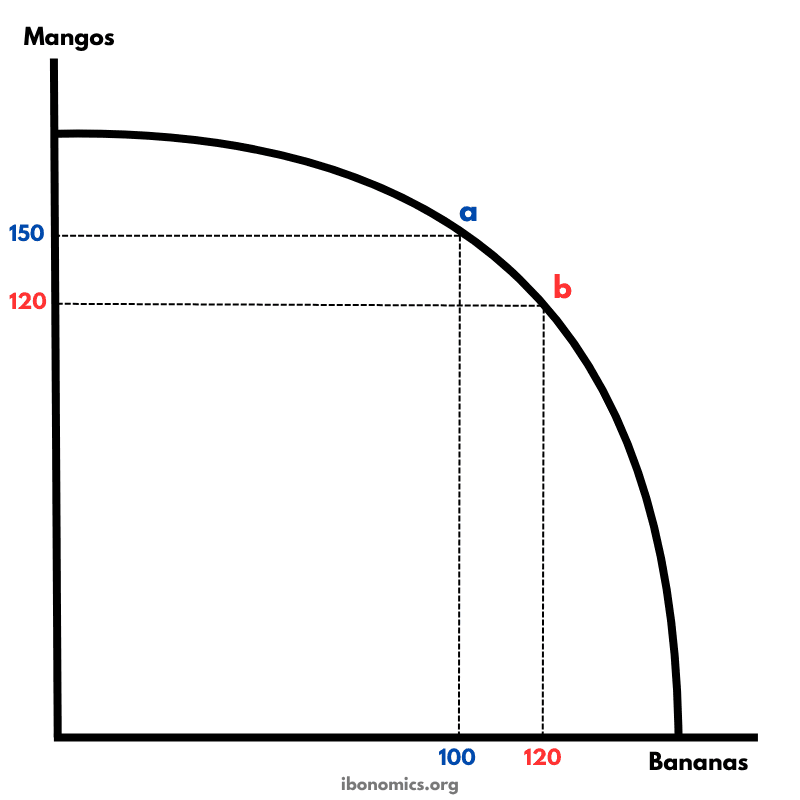
A production possibility curve illustrating the concept of opportunity cost and the trade-offs between producing two goods: mangos and bananas.
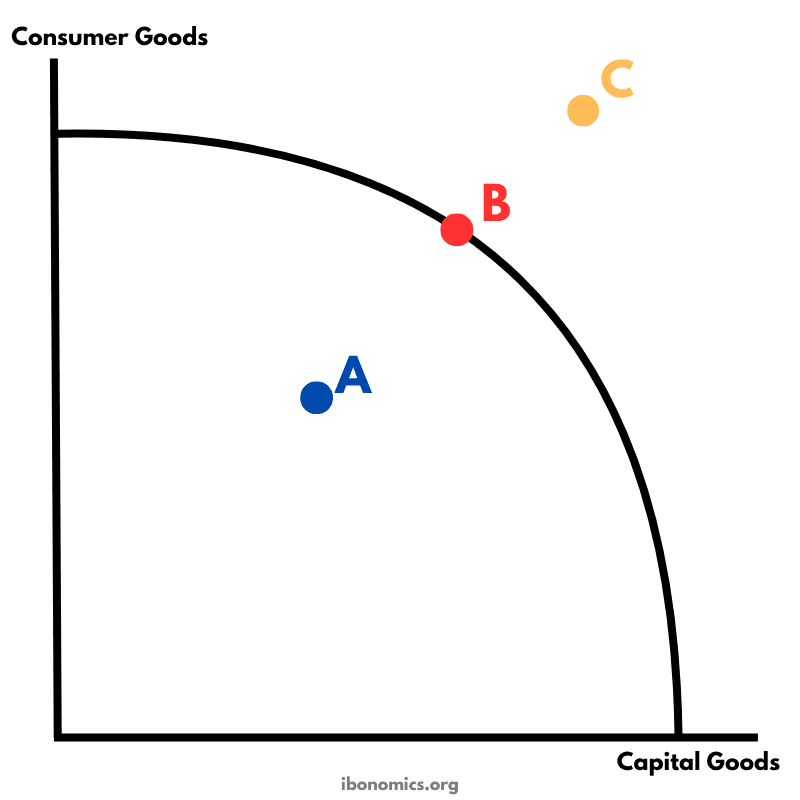
A PPC diagram showing different levels of production efficiency and economic feasibility using combinations of consumer and capital goods.
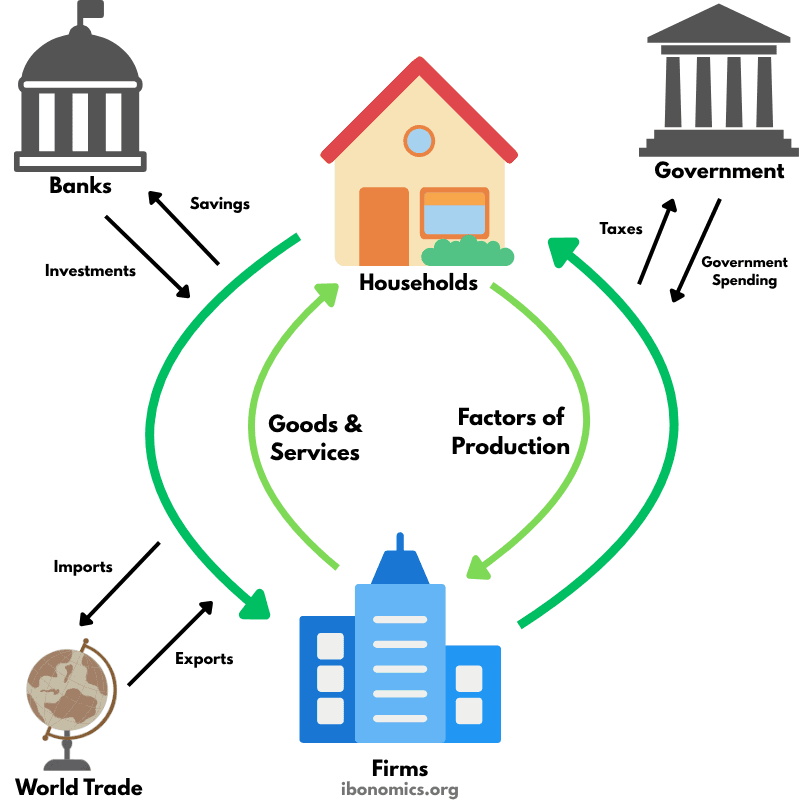
A model illustrating how money, goods, services, and resources flow between households, firms, the government, the financial sector, and the foreign sector in an economy.
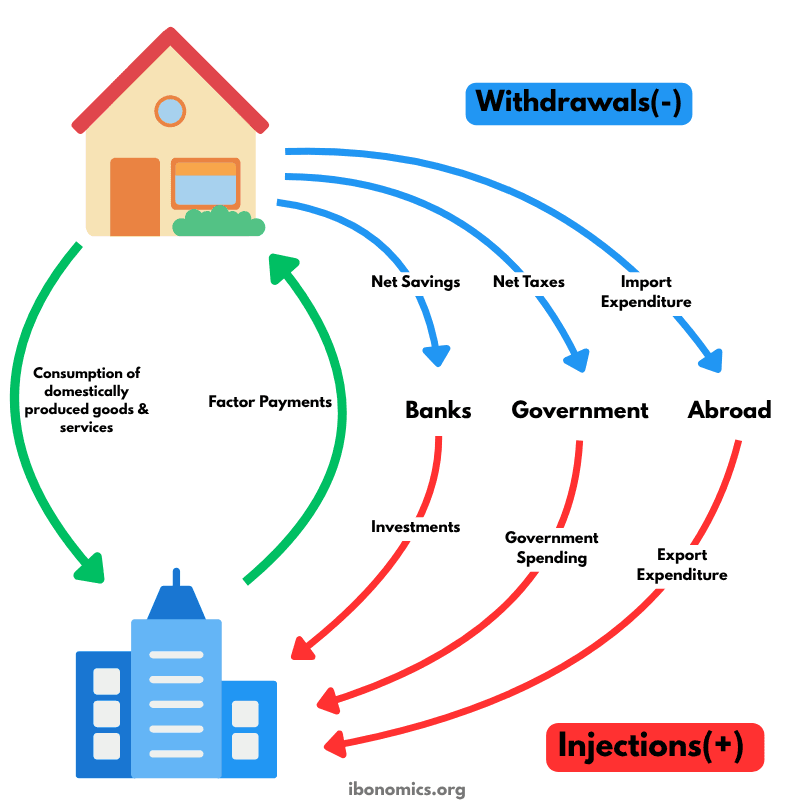
A refined circular flow model highlighting the roles of injections and withdrawals in determining national income and economic equilibrium.