Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
Welcome to IBonomics! We are excited to launch and hope you find the website useful! Learn more about us here!
This diagram shows the intersection of the aggregate demand (AD) and short-run aggregate supply (AS) curves to determine the equilibrium price level and real GDP.
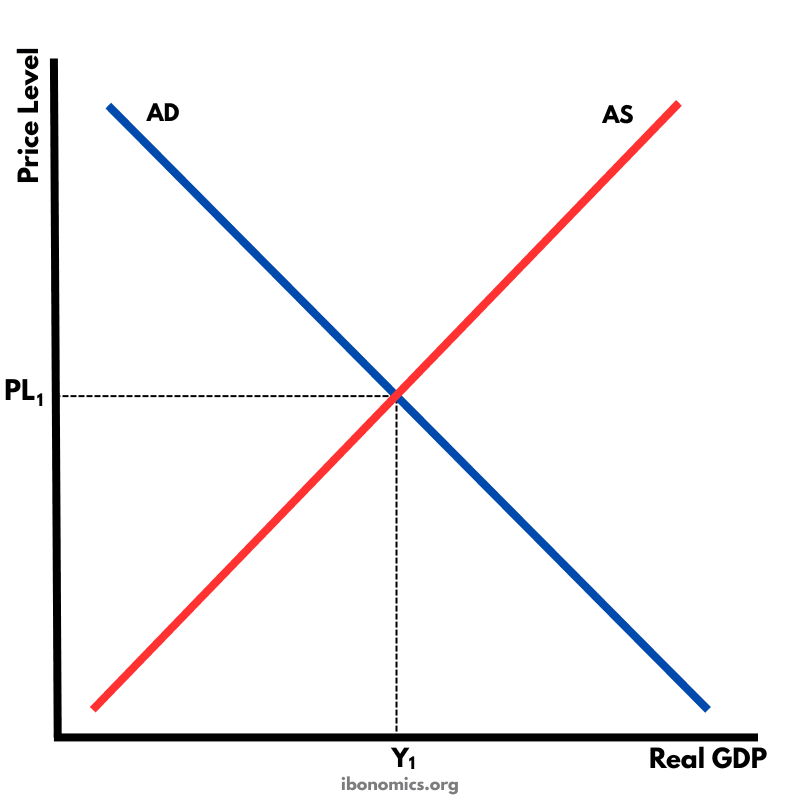
AD: Aggregate Demand, slopes downward due to the wealth effect, interest rate effect, and net export effect.
AS: Aggregate Supply in the short run, slopes upward as higher prices encourage greater output.
PL1: The equilibrium price level where AD intersects AS.
Y1: The equilibrium real GDP/output level where AD equals AS.
Aggregate demand (AD) represents total demand for goods and services in an economy at different price levels.
Aggregate supply (AS) in the short run shows the total quantity of goods and services firms are willing to produce at different price levels.
The intersection of AD and AS determines the macroeconomic equilibrium, with equilibrium price level PL1 and output Y1.
Any shift in AD or AS can cause inflationary or deflationary pressure and impact real GDP.
This model is used to analyze the effects of demand-side or supply-side shocks, as well as the role of fiscal and monetary policy.
Explore other diagrams from the same unit to deepen your understanding

A diagram illustrating the fluctuations in real GDP over time, including periods of boom, recession, peak, and trough, relative to the long-term trend of economic growth.

A diagram showing the Classical model of aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS), used to explain long-run macroeconomic equilibrium.

A Keynesian aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply (AD–LRAS) diagram showing how real GDP and the price level interact across different phases of the economy, including spare capacity and full employment.

A diagram showing an output (deflationary) gap, where the economy is producing below its full employment level of output (Ye).
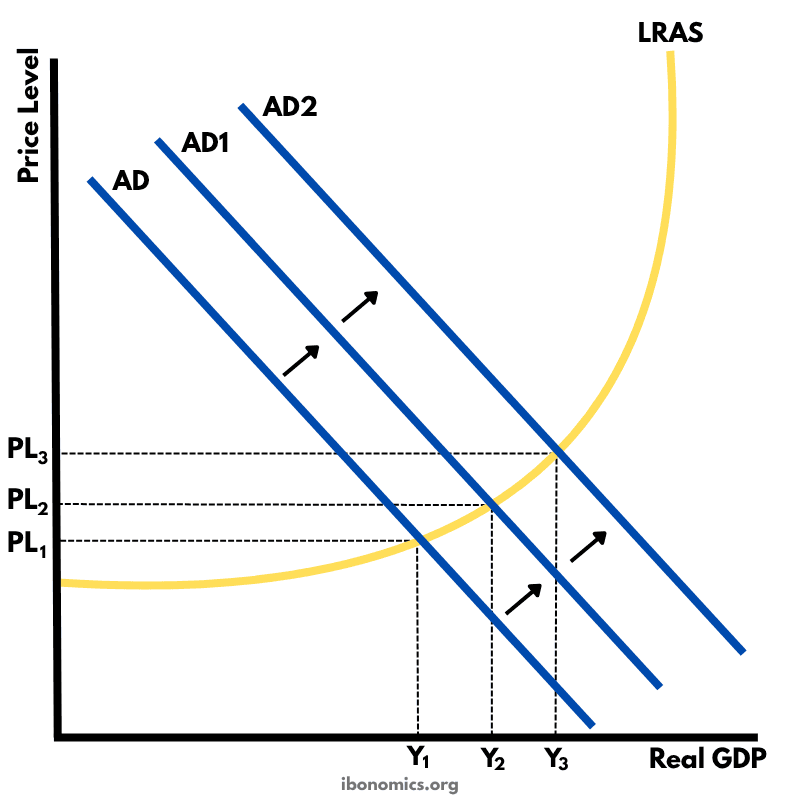
This diagram shows how an initial increase in aggregate demand leads to a multiplied increase in national output (real GDP) and price level within the Keynesian framework.
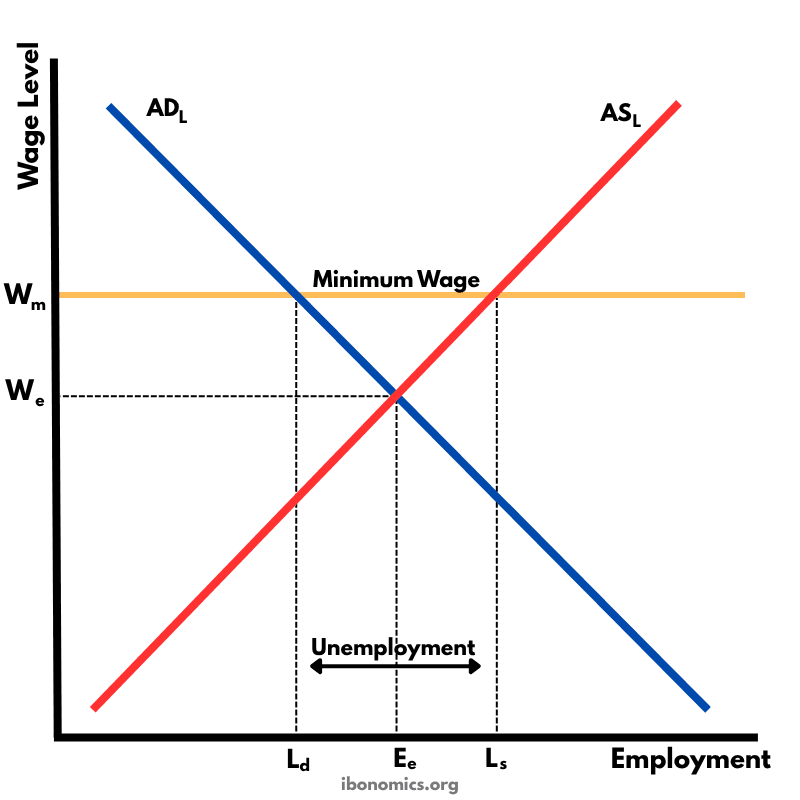
This diagram shows how a government-imposed minimum wage above the equilibrium wage causes excess supply of labour, resulting in unemployment.